CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. —
It's been 59 years since the first person flew into space.
Since then, there have been eight different spacecraft that have carried humans into Earth orbit and beyond. SpaceX's Crew Dragon capsule is about to be the ninth.
Wednesday's tentative launch (weather pending) of the Crew Dragon capsule carrying two American astronauts atop a Falcon 9 rocket will be a historic one for many reasons. SpaceX will be the first commercial company to send NASA astronauts to space, and this will be the first launch of American astronauts from American soil since the last Space Shuttle launch in 2011.
With all eyes on the skies for the launch of astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley to the International Space Station, here's a look back at the history of crewed spaceships:

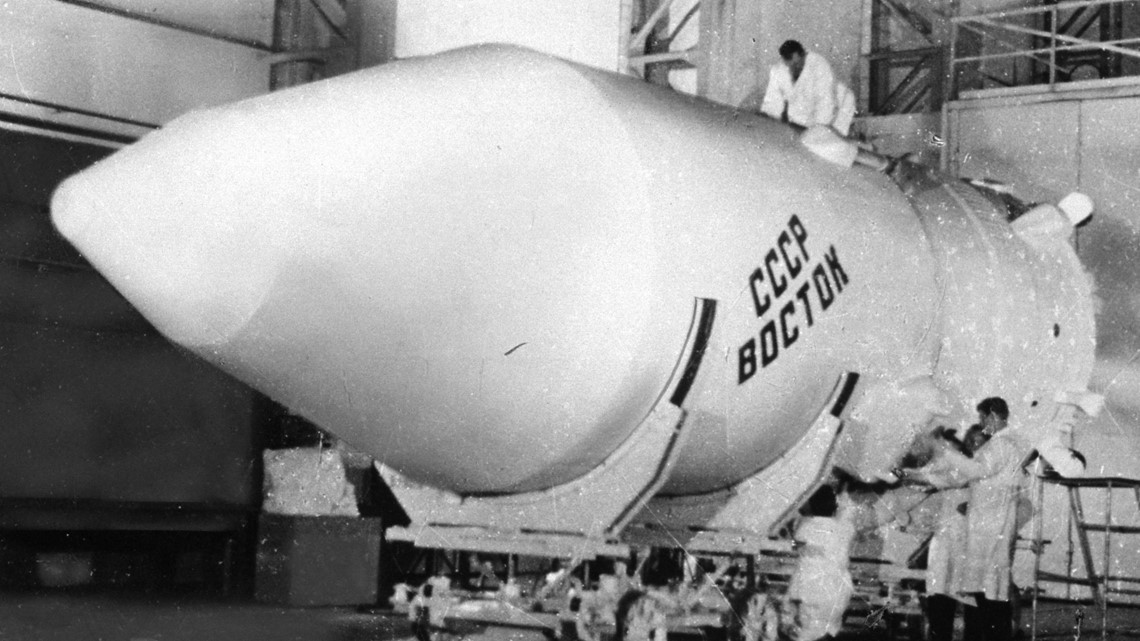
Vostok,1961
The Soviet Union's first spaceflight program also saw the launch of the first human into space -- Yuri Gagarin on April 12, 1961. The Vostok 1 was built to carry just one person and had no landing gear. There was also a window near Gagarin's feet to let him see the Earth during the flight.

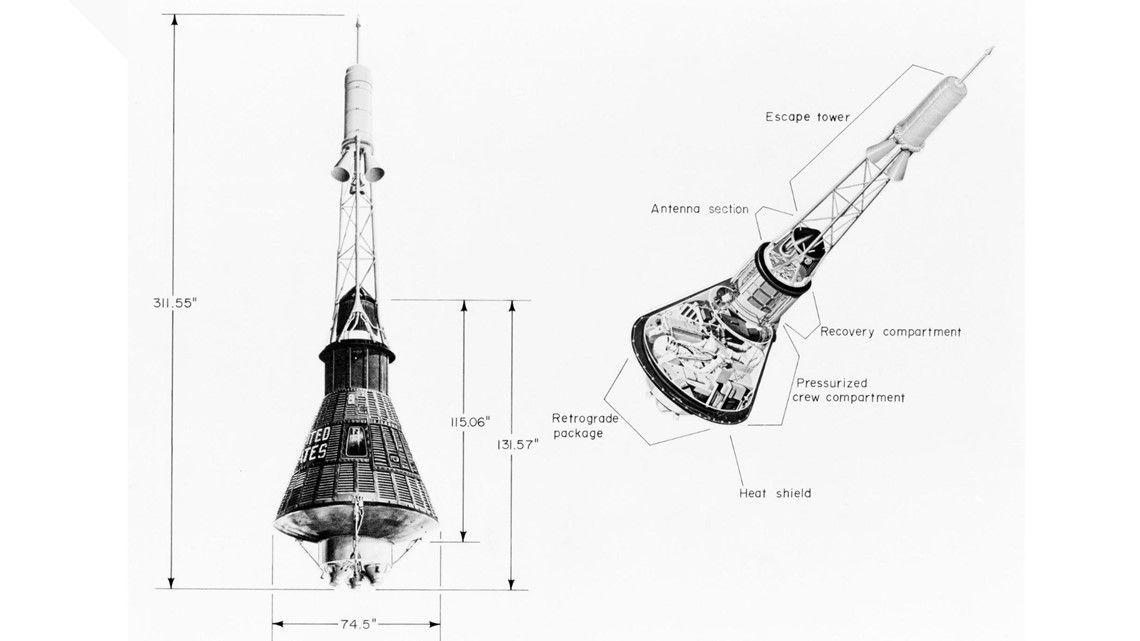
Mercury, 1961
The first American spaceship was a cone-shaped capsule that carried just one person. The Mercury spacecraft was 6 feet, 10 inches long and 6 feet, 2.5 inches in diameter. There was also a 19-foot, 2-inch escape tower attached to its cylinder.
Three weeks after the Soviet Union launched Gagarin into space, astronaut Alan Shepard became the first American on a suborbital flight. Astronaut John Glenn reached orbit in February 1962 with the Mercury and the Friendship 7 capsule.

Voskhod 1964
This spacecraft was similar to the Vostok, but it was able to carry more crewmembers and eventually help make the first spacewalk happen. The Soviet Union also nabbed the record for the first spacewalk thanks to the Voskhod 2 in 1965 when Alexei Leonov spent about 12 minutes in space.
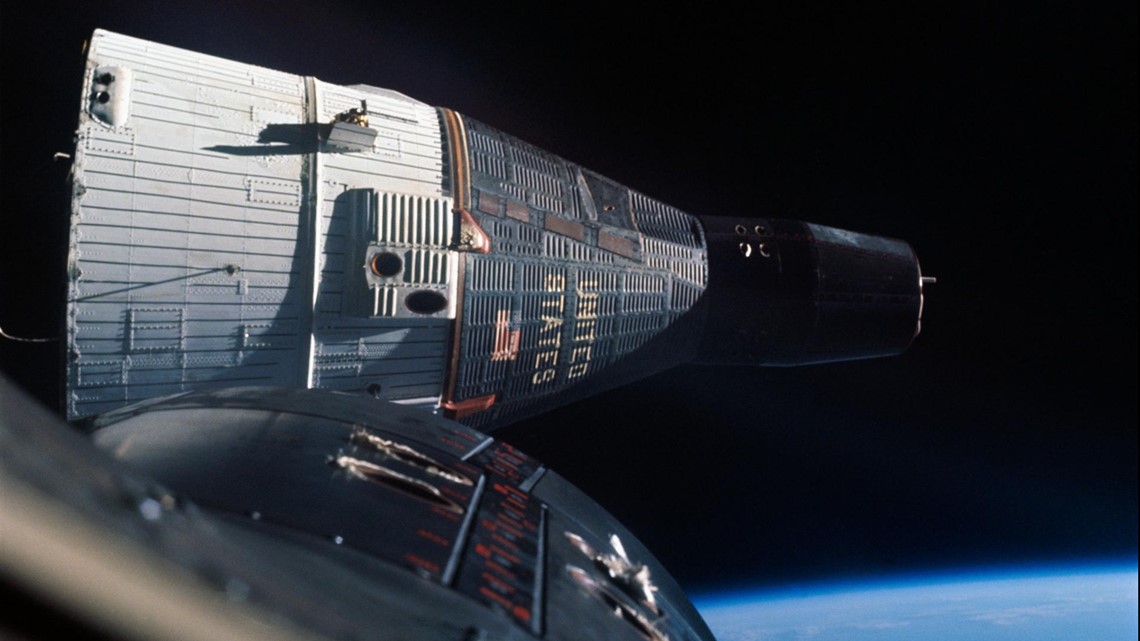


Gemini, 1965
Like Voskhod, Gemini was also adapted to fit more humans inside. And, since this was at the height of the first space race between the U.S. and the Soviet Union, Gemini first flew days after the Voskhod 2 spacewalk mission.
Gemini spacecraft fit two astronauts and was instrumental in teaching engineers how to dock in orbit and extending the duration of time humans could spend in space. Gemini led to the first American spacewalker, Ed White, who spent 23 minutes in space.
Between 1965 and 1966, there were 10 crews and 16 individual astronauts who flew in low-Earth orbit during Gemini missions.


Soyuz 1967
While the Soyuz capsule still ferries cosmonauts (and, until Crew Dragon, astronauts) back and forth to the International Space Station, the spacecraft was first developed in 1967. However, the Soyuz of today looks much different from the ones used in the 1960s.
There are three main parts of the Soyuz: The descent module is where the space travelers sit during launch and is the only part that returns to Earth, the orbital module includes crew living space and the docking system and the propulsion module carries engines, fuel and solar panels.
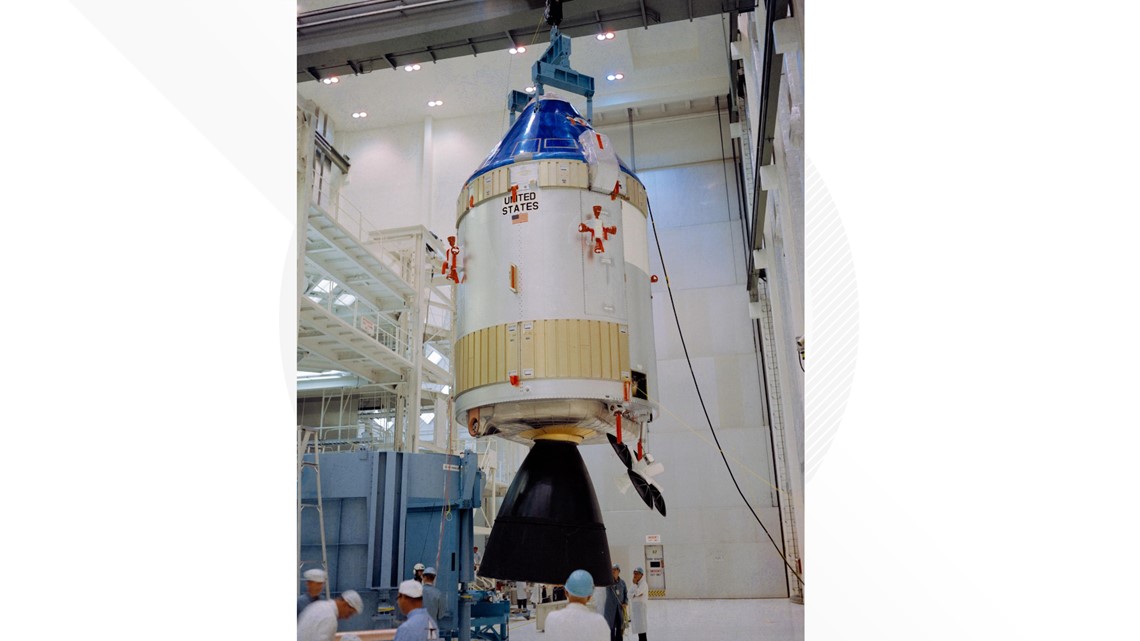


Apollo 1968
Perhaps the most famous spacecraft in the world, Apollo capsules were the ones who helped land humans on the moon for the first time. The spacecraft was more squat and conical in shape than Mercury and Gemini but were designed to carry even more astronauts, including the 12 people who have walked on the lunar surface.
The Apollo command module was only meant for transportation to and from Earth. The lunar module was able to attach and detach from the "Columbia" command module to ferry Apollo 11 astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin to the moon in 1969.
The Apollo era ended with the Apollo 17 mission in December 1972 and a final flight in 1975.
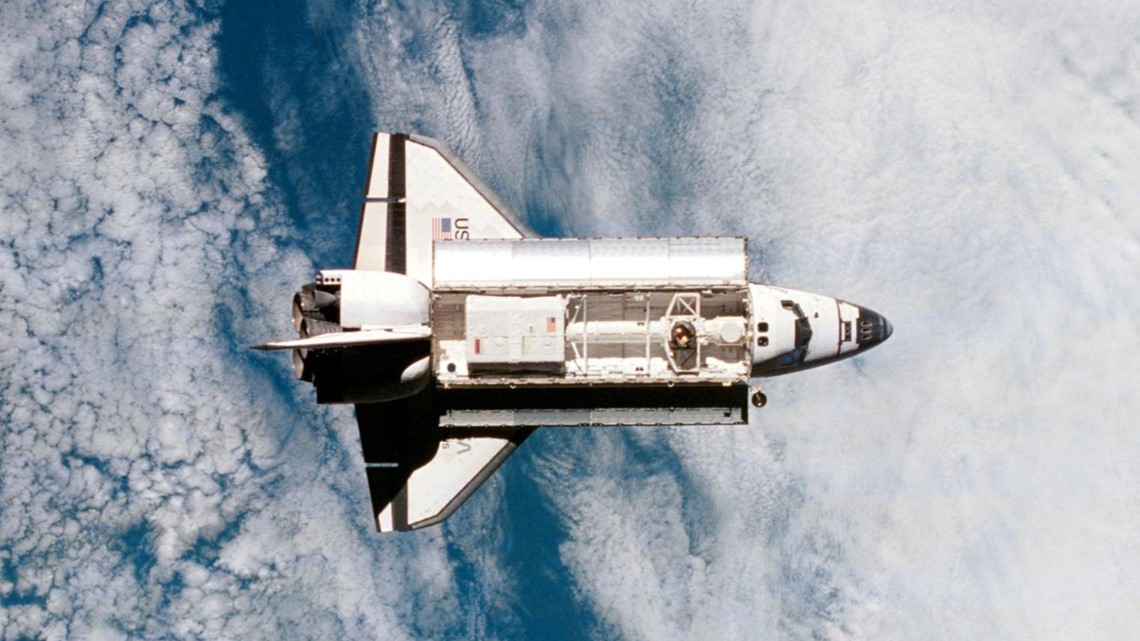


Space Shuttle 1981
The Space Shuttle was the largest crewed spacecraft and the first reusable one. Between 1981 and 2011, there were five different shuttles and 135 crewed missions. These missions helped construct the International Space Station and the Hubble telescope and launched and repaired satellites.
The main body of the shuttle, which looks like a plane and has similar landing gear, was also the orbiter. To launch the space shuttle, a massive rust-colored fuel tank and two smaller solid rocket boosters were used.
The space shuttle, technically called the Space Transportation System, was able to carry seven astronauts to space and also protect them from the burn of re-entry to Earth.
The space shuttle era ended on July 21, 2011, when Atlantis returned to Kennedy Space Center.
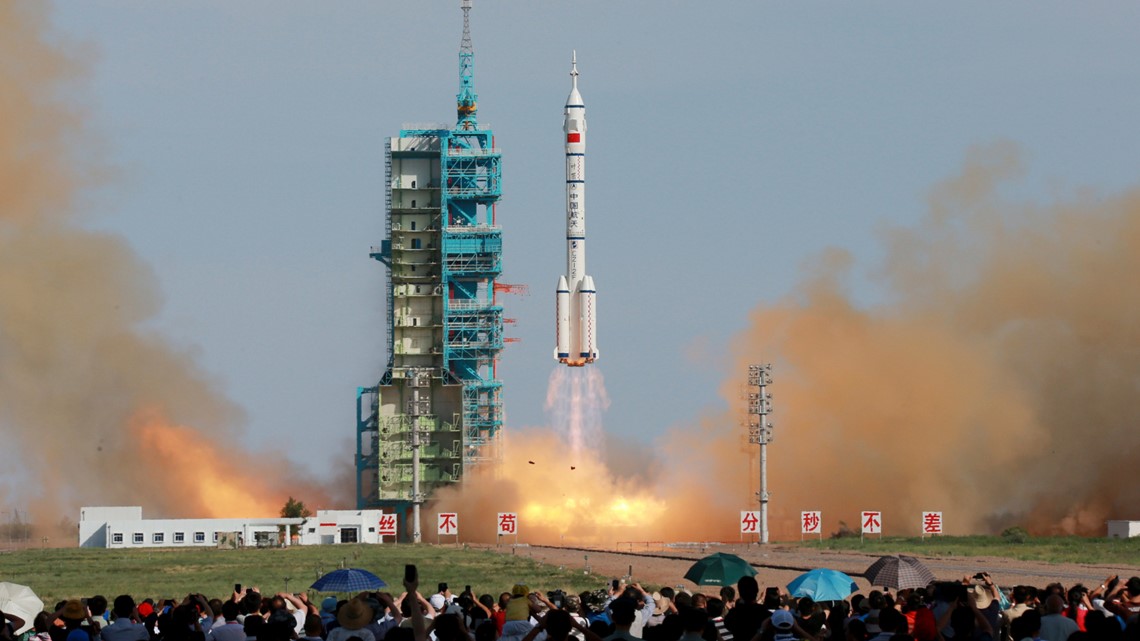


Shenzhou, 2003
China's spacecraft looks similar to the Russian Soyuz capsule but is slightly larger. It also has three parts: the orbital module, the re-entry module and the service module. Though the country launched its first efforts for space exploration in 1968, the first crewed launch of the Shenzhou wasn't until 2003 during the Shenzhou 5 mission.
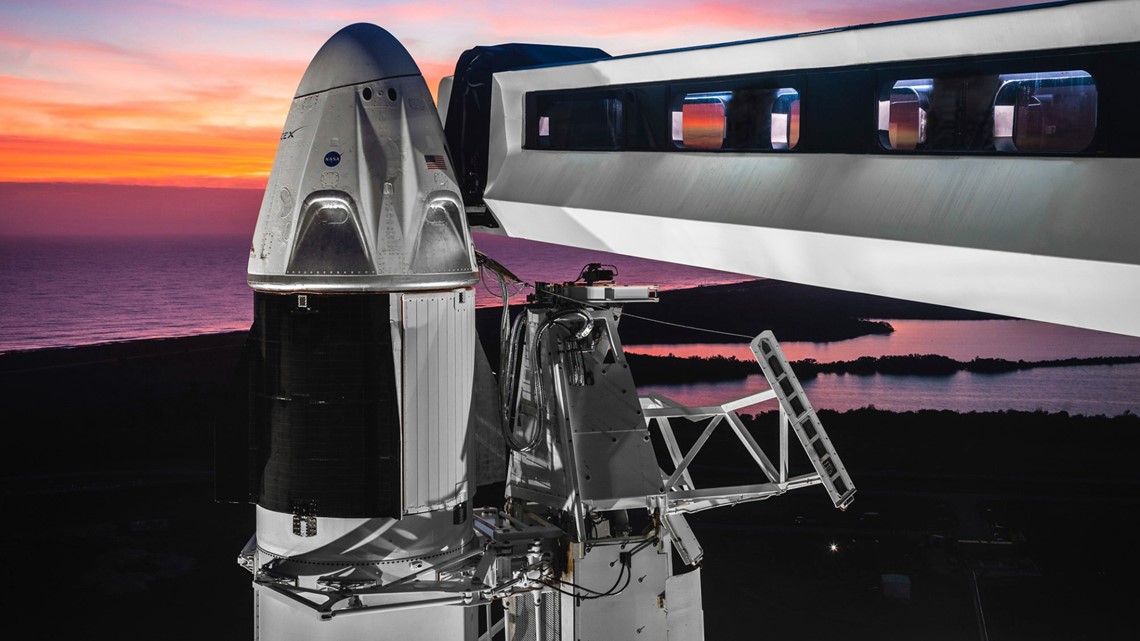


Crew Dragon, 2020
Like the Space Shuttle, SpaceX's Dragon capsule can carry up to seven astronauts. It's also meant to be reused. However, the Dragon spacecraft will be the first used by a commercial company as opposed to a government agency like NASA.
The Dragon capsules have also been used to carry cargo to and from the ISS as part of the public-private collaboration with NASA.
The spacecraft is more than 26 feet tall, 13 feet in diameter and is 328 square feet inside. The capsule is also able to launch more than 13,000 pounds of payload.
While it can hold up to seven, Dragon's first crewed mission will have just two astronauts headed to the ISS.
What other people are reading right now:
- Researchers track high levels of COVID-19 in Florida wastewater
- Floridians can get 13 additional weeks of unemployment under federal program
- World Redhead Day is May 26! 12 fun facts about red hair
- Weather forecast looks iffy for historic SpaceX, NASA launch
- 3 adults, 3 children ejected during deadly rollover crash near Orlando
- Mayor: 4 Minneapolis police officers involved in death of George Floyd terminated
FREE 10 TAMPA BAY APP:
►Stay In the Know! Sign up now for the Brightside Blend Newsletter



